What Is Router in Networking And How It Works: The Ultimate Guide
A router is a networking device that directs data packets between different computer networks. It works by analyzing the destination IP address of each packet and determining the most efficient path for it to reach its destination.
The router then forwards the packets along this path, ensuring that they arrive at the intended destination. Routers play a crucial role in connecting multiple networks and enabling communication between devices on different networks. They also provide functionalities such as network address translation (NAT), firewall protection, and quality of service (QoS) management.
Overall, routers facilitate efficient and secure data transmission in a networked environment.
Understanding The Basics Of Networking
The fundamentals of networking
In today’s digital age, networking has become an essential part of our everyday lives. Whether it’s at home, in the office, or even on the go, we rely on networks to connect our devices and enable communication and information sharing. But what exactly is networking and how does it work? To understand this, let’s dive into the basics.
Components of a network
At its core, a network is a collection of interconnected devices that communicate with each other. These devices can range from computers, smartphones, tablets, and servers to printers, IoT devices, and more. To enable communication within a network, each device is assigned a unique identifier called the IP address.
In addition to devices, networks consist of various other components. These include:
- Routers: These devices play a crucial role in networking and are responsible for directing network traffic and ensuring that data packets reach their intended destinations. We will discuss routers in more detail shortly.
- Switches: Switches facilitate communication between devices within a local area network (LAN). They create multiple connections between devices, allowing for efficient data transfer.
- Modems: Modems connect a network to the Internet by establishing a connection with the Internet Service Provider (ISP). They enable the transmission of data between the network and the Internet.
- Gateways: Gateways act as intermediaries between different networks, allowing communication between networks with different protocols or technologies.
The role of routers in networking
Routers are the backbone of any network infrastructure. They are responsible for routing data packets between different networks, ensuring that information is transmitted accurately and efficiently. A router analyzes the destination IP address of each packet and determines the best path for it to reach its destination.
Routers use a routing table, which contains information about various network destinations and the paths to reach them. Based on this information, routers make intelligent decisions regarding packet forwarding. They consider factors such as network congestion, link availability, and the shortest path to its destination.
In addition to routing, routers also provide features such as network address translation (NAT), which allows multiple devices in a network to share a single IP address when communicating with external networks. They also offer firewall capabilities to enhance network security.
Overall, routers are crucial components of networking that enable devices to communicate with each other and with the Internet. Without routers, the seamless flow of data across networks would not be possible.
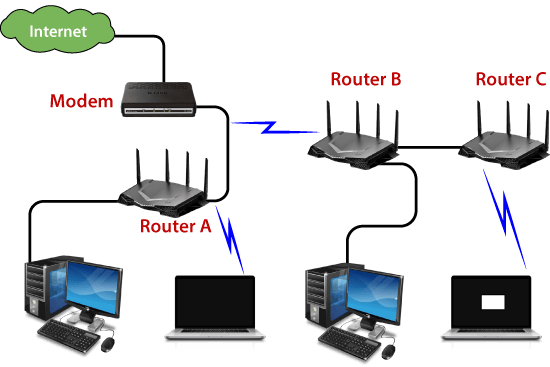
Image credit: javatpoint.com
How Does A Router Function In A Network?
The primary functions of a router
A router is a vital component in computer networking that plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient and effective communication between devices within a network. These devices can include computers, mobile phones, smart TVs, and other internet-enabled devices. By directing data packets to their intended destinations, routers enable seamless connectivity and allow for the transmission of information. But what are the main functions of a router? Let’s take a closer look.
Routing data packets
One of the key functions of a router is to route data packets within a network. When a device in a network sends information to another device, the data is split into small packets that are then transmitted individually. These packets travel across the network and reach their destination by following the most efficient path. It is the router’s responsibility to determine this path and direct the packets accordingly. Routers accomplish this by maintaining a routing table that contains information about the network’s topology and the best paths to different destinations.
This routing process allows routers to efficiently distribute data packets across a network, ensuring that they reach the intended recipient promptly. Routers use various routing protocols, such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) or Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), to determine the optimal path for data transmission. By continuously evaluating network conditions and utilizing these protocols, routers can adapt to changes in the network and make real-time routing decisions.
Managing network traffic
Another critical function of a router is to manage network traffic. In a network, multiple devices are typically connected and actively using the network’s resources simultaneously. This can lead to congestion and a decrease in network performance if not properly managed. Routers help alleviate this issue by implementing traffic management techniques.
Routers utilize Quality of Service (QoS) algorithms to prioritize traffic and allocate bandwidth based on the specific needs of different types of data. For example, real-time applications like voice and video calls require low latency and high bandwidth, while file downloads can tolerate longer latency. By intelligently prioritizing and managing network traffic, routers ensure that each device and application receives the necessary resources for optimal performance.
Routers also employ techniques such as network address translation (NAT) to provide an additional layer of security and enhance network efficiency. NAT allows multiple devices within a local area network (LAN) to share a single public IP address by dynamically translating private IP addresses to the public address when communicating with external networks.
In conclusion, routers are integral to the functioning of computer networks. They perform vital tasks such as routing data packets, managing network traffic, and ensuring efficient communication between devices within a network. By fulfilling these functions, routers facilitate seamless connectivity and contribute to a smooth and reliable network experience.
| Key Functions of a Router |
|---|
| Routing data packets |
| Managing network traffic |
- Routers determine the most efficient paths for data packets to reach their destinations.
- Routers use routing protocols to make real-time routing decisions.
- Routers manage network traffic by prioritizing and allocating bandwidth based on the needs of different types of data.
- Routers employ techniques such as network address translation (NAT) for added security and network efficiency.
The Working Mechanism of a Router
Packet forwarding process
One of the key functions of a router is the packet forwarding process. When a packet arrives at the router, it examines the destination IP address to determine the best path for forwarding the packet. This process is crucial in ensuring that the packet reaches its intended destination efficiently and quickly.
The packet forwarding process involves several steps:
- First, the router receives the incoming packet.
- The router then checks the routing table to find the best next hop for forwarding the packet.
- Once the next hop is determined, the router encapsulates the packet in a new frame with the appropriate destination MAC address.
- The encapsulated packet is then transmitted to the next hop.
- This process continues until the packet reaches its final destination.
Routing tables and protocols
Routing tables play a crucial role in the functioning of a router. These tables contain information about the networks and their corresponding next hops. The router uses this information during the packet forwarding process to determine the best path for each packet.
Various routing protocols facilitate the exchange of routing information between routers. These protocols help routers build and update their routing tables, ensuring that they have the most up-to-date information about the network topology. Some commonly used routing protocols include:
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
- Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Network layer operations
The network layer is responsible for the logical addressing and routing of packets. In a router, the network layer performs various operations to ensure efficient packet forwarding:
- Packet encapsulation: When a packet arrives at the router, it must be encapsulated in a new frame with the appropriate source and destination MAC addresses.
- IP address assignment: The router assigns unique IP addresses to devices connected to its network. This allows for proper communication between devices.
- IP routing: Using the information in the routing table, the router determines the best path for each packet and forwards it accordingly.
In conclusion, a router plays a critical role in computer networks by effectively forwarding packets based on routing tables and protocols. Its network layer operations ensure efficient communication between devices connected to the network.
Types Of Routers And Their Purposes
When it comes to networking, routers play a crucial role in connecting devices and facilitating data transmission. Routers are versatile devices that come in different types, each serving specific purposes. In this section, we will explore the different types of routers and their benefits.
Wireless Routers and Their Benefits
Wireless routers, as the name suggests, allow for wireless connectivity within a network. They utilize Wi-Fi technology to provide internet access to devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets. Wireless routers are ideal for homes and small businesses where mobility is essential. The benefits of wireless routers include:
- Flexibility and convenience, allowing users to connect their devices without the need for cables
- Easy setup and configuration, simplifying the process of connecting multiple devices
- Ability to cover a wide area, providing seamless internet access throughout the premises
- Support for multiple devices, enabling simultaneous connections for various users
Core Routers for Large-scale Networks
Core routers are designed for large-scale networks and serve as the backbone of the internet. They are responsible for handling significant amounts of traffic and ensuring data is properly routed between networks. Core routers are typically used by internet service providers (ISPs) and large organizations. Some benefits of core routers include:
- High-speed data transmission, allowing for efficient communication between networks
- Advanced routing protocols and algorithms, ensuring optimal network performance
- Scalability, enabling them to handle increasing network traffic without compromising speed
- Redundancy features, ensure uninterrupted connectivity even in the event of hardware failures
Wired Routers for Stable Connections
Wired routers, also known as Ethernet routers, provide stable connections by utilizing wired connections such as Ethernet cables. These routers are commonly used in environments where a stable and reliable connection is crucial, such as offices and data centers. The benefits of wired routers include:
- Higher security levels compared to wireless routers, as wired connections are less susceptible to interference
- Lower latency and faster data transfer speeds, making them ideal for bandwidth-intensive tasks
- Ability to handle large amounts of data traffic without experiencing performance degradation
- Support for a wide range of devices and network configurations
In conclusion, routers come in various types, each serving specific purposes in networking. Wireless routers provide flexibility and convenience, core routers handle large-scale network traffic, and wired routers offer stability and reliability. Understanding the different types of routers helps in choosing the most suitable one for your networking needs.
Key Features And Capabilities Of Routers
Quality of Service (QoS)
One of the key features of routers is their ability to prioritize network traffic using Quality of Service (QoS). QoS allows routers to allocate bandwidth and assign priority levels to different types of traffic, ensuring that critical data and applications receive the necessary resources for optimal performance.
With QoS, routers can differentiate between different types of traffic, such as VoIP calls, video streaming, and web browsing. By prioritizing important traffic over less critical traffic, routers can ensure that real-time applications, like voice and video calls, experience minimal latency and packet loss, delivering a seamless user experience.
Network Security Features
Routers are also equipped with various network security features to protect your network from unauthorized access and potential threats. These security features help safeguard sensitive data and ensure the integrity of your network.
Some common network security features found in routers include:
- Firewall: Routers often include a built-in firewall that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and blocks any suspicious or malicious activity.
- VPN Support: Many routers offer Virtual Private Network (VPN) support, allowing remote users to connect securely to your network over an encrypted tunnel.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Some advanced routers feature intrusion detection and prevention systems that analyze network traffic for signs of potentially harmful activity and take action to mitigate risks.
- Content Filtering: Routers can also provide content filtering capabilities, allowing administrators to restrict access to certain websites or types of content.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT) is another essential capability of routers. NAT allows multiple devices on a private network to share a single public IP address, enabling them to access the internet.
By assigning private IP addresses to devices within a local area network (LAN), routers can translate these addresses into a single public IP address when communicating with devices on the internet. This process aids in preserving IP address space and adds an additional layer of security by hiding internal IP addresses from external networks.
Thanks to NAT, routers allow multiple devices with private IP addresses to communicate with external networks and the internet without needing a pubess for each individual device.
Understanding Router Configuration And Setup
A router plays a crucial role in networking by directing data packets between different networks. Besides providing internet access to multiple devices, routers also enable communication between devices within the same network. To ensure a seamless and secure connection, it is essential to understand how to configure and set up your router correctly.
Accessing the router’s admin panel
Accessing the router’s admin panel is the first step in configuring and setting up your router. To do this, follow these simple steps:
- Connect your computer or device to the router using an Ethernet cable or via a wireless connection.
- Open a web browser and enter the default IP address of the router in the address bar. Common default IP addresses include 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1.
- You will be prompted to enter a username and password to log in to the admin panel. If you haven’t changed these credentials, you can refer to the router’s documentation or use common default usernames and passwords provided by the manufacturer.
- Once logged in, you will have access to the router’s configuration settings and various options to customize your network.
Configuring network settings
After accessing the router’s admin panel, you can configure the network settings to optimize your network performance. Here are some important settings to consider:
- Network name (SSID): Choose a unique and memorable name for your network to easily identify it.
- Security settings: Enable a strong encryption method such as WPA2-PSK to protect your network from unauthorized access.
- IP addressing: Decide whether to use DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to automatically assign IP addresses to devices or use static IP addresses for more control over your network.
- Port forwarding: Configure port forwarding to allow specific applications or services to bypass the router’s firewall and communicate with devices on your network.
Setting up wireless connections
If you want to connect your devices wirelessly to the router, setting up wireless connections is essential. Here are the steps to follow:
- Navigate to the wireless settings section in the router’s admin panel.
- Choose an appropriate Wi-Fi channel to avoid interference from neighboring networks.
- Set a strong password for your wireless network to prevent unauthorized access.
- Consider enabling features like MAC address filtering or guest network to enhance security and control access to your network.
By following these steps, you can effectively configure and set up your router, ensuring a stable and secure network for all your devices. Remember to regularly update your router’s firmware to benefit from the latest security patches and performance improvements.
Common Router Issues And Troubleshooting Techniques
Slow Internet Speed and Connection Drops
One of the most common issues that users face with their routers is slow internet speed and frequent connection drops. This can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you are in the middle of an important task or trying to enjoy streaming content.
Possible Causes
There are several factors that can contribute to slow internet speed and connection drops:
- Network Congestion: If multiple devices are connected to the router and consume a lot of bandwidth, it can slow down the internet speed for all devices.
- Interference: Other electronic devices, such as cordless phones and microwaves, can interfere with the Wi-Fi signal, leading to a weaker connection.
- Distance from Router: If you are too far away from the router, the Wi-Fi signal may not reach your device at full strength, resulting in slower speeds.
- Outdated Router Firmware: Router firmware updates are essential to ensure optimal performance and fix any known bugs or vulnerabilities.
Troubleshooting Steps
To troubleshoot slow internet speed and connection drops, follow these steps:
- Check Network Congestion: If multiple devices are connected to the router, try disconnecting some of them or limiting their bandwidth usage to improve overall internet speed.
- Reduce Interference: Keep electronic devices that may interfere with the Wi-Fi signal away from the router. Additionally, consider changing the Wi-Fi channel to minimize interference from neighboring networks.
- Reposition Router: Try moving the router to a central location in your home or office to improve Wi-Fi coverage and signal strength.
- Update Router Firmware: Access your router’s admin panel and check for any available firmware updates. If updates are available, install them to ensure optimal performance and stability.
Router Firmware Updates and Troubleshooting Steps
Keeping your router’s firmware up to date is crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient network. Firmware updates often include bug fixes, performance improvements, and new features.
Steps to Update Router Firmware
To update your router’s firmware, follow these steps:
- Access Router Admin Panel: Open a web browser and enter the router’s IP address in the address bar. Log in using your router’s admin credentials.
- Check for Updates: Look for a Firmware or Software Update section in the admin panel. Check for any available updates.
- Download and Install Update: If a firmware update is available, download it from the manufacturer’s website. Follow the instructions provided to install the update.
- Restart Router: After installing the firmware update, restart the router to apply the changes.
Dealing with Router Hardware Failures
While router hardware failures are relatively rare, they can happen and cause disruptions to your internet connectivity. It’s important to be aware of the signs of hardware failures and take appropriate action.
Possible Hardware Failures
Some common router hardware failures include:
- Power Supply Issues: If the router is not receiving adequate power, it may not function properly.
- Router Overheating: Continuous usage and poor ventilation can cause routers to overheat, leading to performance issues or complete failure.
- Physical Damage: Accidental drops or spills can damage the router’s internal components, resulting in malfunction.
Troubleshooting Steps
If you suspect a hardware failure, try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check Power Supply: Ensure that the router is properly connected to a power source and the power adapter is functioning correctly.
- Prevent Overheating: Keep the router in a well-ventilated area and avoid placing objects on top of it. If necessary, consider using a cooling pad or fan to prevent overheating.
- Inspect for Physical Damage: Carefully examine the router for any visible signs of physical damage. If found, it may be necessary to replace the router.
Enhancing Network Performance with Router Optimization
Optimizing Router Placement for Better Coverage
Proper router placement is crucial for maximizing network coverage and ensuring a strong and reliable connection throughout your home or office. To optimize router placement, consider the following:
- Place the router in a centralized location to ensure equal coverage in all areas.
- Avoid placing the router near obstructions such as walls, furniture or appliances that may interfere with the signal.
- Elevate the router to improve signal strength, such as on a shelf or wall mount.
- Consider using a Wi-Fi range extender or mesh network system to extend the coverage to hard-to-reach areas.
By optimizing router placement, you can enhance network performance, reduce dead zones, and enjoy seamless connectivity throughout your space.
Updating Router Firmware for Improved Performance
Router firmware plays a crucial role in the overall performance and security of your network. Regularly updating your router’s firmware can help ensure that you have the latest bug fixes, security patches, and performance enhancements. Here are the steps to update your router firmware:
- Check the router manufacturer’s website for the latest firmware version specific to your router model.
- Access your router’s admin interface by typing its IP address into your web browser.
- Locate the firmware update section and follow the instructions provided.
- During the update process, refrain from interrupting or turning off the router to prevent potential damage or instability.
- Once the update is complete, restart the router to apply the changes.
By keeping your router firmware up to date, you can ensure optimal performance, improved security, and access to the latest features and enhancements.
Using Router Management Tools to Monitor and Optimize Network
Router management tools provide invaluable insights into your network’s performance and allow you to make necessary optimizations. Here are some key features and benefits of using router management tools:
| Feature | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Real-time monitoring | Monitor network traffic, bandwidth usage, and connected devices in real-time to identify bottlenecks and troubleshoot issues. |
| Quality of Service (QoS) settings | Prioritize network traffic and allocate bandwidth to specific devices or applications, ensuring a smooth and uninterrupted experience for critical activities. |
| Guest network management | Create separate Wi-Fi networks for guests, ensuring security and protecting your main network. |
| Parental controls | Manage and restrict content or internet access for specific devices or users, providing a safer online environment for children. |
By utilizing router management tools, you can monitor, configure, and optimize your network effortlessly, resulting in improved performance, security, and control.
Advanced Router Features For Network Professionals
Network professionals rely on advanced router features to optimize and secure their networks. These features go beyond the basic functions of a router and enable professionals to create more efficient and robust networks. In this article, we will explore three advanced router features that are essential for network professionals: virtual routers (V-Routers) for virtual networking, load balancing and link aggregation, and configuring VPNs on routers for secure remote access.
Virtual routers (V-Routers) for virtual networking
Virtual routers, also known as V-Routers, are crucial for network professionals who work with virtual networks. V-Routers allow for the creation of multiple virtual networks within a physical network infrastructure. This enables network administrators to partition their networks and allocate resources more efficiently.
A V-Router operates as a virtual machine or a software-based router, simulating the functions of a physical router. It can perform all the routing tasks, including routing protocols, forwarding packets, and managing network traffic. The ability to create virtual networks within a physical infrastructure offers flexibility and scalability, making it easier for network professionals to manage complex networks.
Load balancing and link aggregation
Load balancing and link aggregation are advanced router features designed to optimize network performance and ensure high availability. Load balancing distributes network traffic across multiple network links, preventing any single link from becoming overloaded. This helps to improve overall network performance and prevents bottlenecks that can slow down data transmission.
Link aggregation, on the other hand, combines multiple network links into a single logical link. This increases bandwidth capacity and provides redundancy in case of link failure. Network professionals can configure link aggregation to ensure that network traffic is evenly distributed and to provide failover capabilities, enhancing network reliability and performance.
Configuring VPNs on routers for secure remote access
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are crucial for network professionals who require secure remote access to their networks. By configuring VPNs on routers, professionals can establish encrypted connections between remote locations or remote users and their network infrastructure.
VPN configurations on routers provide a secure tunnel for data transmission, preventing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive information. This allows network professionals to securely access their networks from anywhere, ensuring connectivity and productivity even when working remotely.
Additionally, VPNs on routers enable secure communication between different network locations, creating virtual private networks within a larger network infrastructure. This is particularly beneficial for organizations with multiple branch offices or remote workers, as it allows for secure and seamless data exchange between different network segments.
Overall, network professionals can leverage these advanced router features to optimize network performance, ensure high availability, and enhance network security.
Router Vs. Modem: Differentiating The Two Devices
Explaining the roles of modems and routers in networking
In order to understand the differences between a router and a modem, it is important to first understand their individual roles in a network. A modem, short for modulator-demodulator, is responsible for connecting your home network to your internet service provider (ISP). It essentially acts as the gateway between your ISP and your devices, allowing you to access the internet. On the other hand, a router is a device that enables all of your wired and wireless devices to use and share the internet connection provided by the modem. It allows devices within your network to communicate with each other directly and facilitates the smooth flow of data.
How modems and routers work together
Modems and routers work together to create a seamless networking experience. The modem establishes a connection with your ISP and receives an IP address, which is a unique identifier for your network. The router then takes this internet connection and gives access to all the connected devices in your network. It acts as a central hub, directing and managing the flow of data between devices and the internet. By assigning local IP addresses to each device connected to the network, the router ensures that data packets reach their intended destinations accurately and efficiently.
Choosing the right modem and router for your network
When it comes to setting up a network, choosing the right modem and router is crucial. This decision will directly impact the performance and reliability of your network connection. When selecting a modem, it is important to consider factors such as compatibility with your ISP, data transfer speed, and number of ports available. The router, on the other hand, should be capable of providing sufficient wireless coverage and support for the number of devices you have. Additionally, security features such as firewall protection and encryption are essential to protect your network from unauthorized access.
In conclusion, understanding the roles of modems and routers in networking is essential for creating a reliable and efficient network. While modems connect your network to your ISP, routers enable devices within the network to communicate and share the internet connection. By selecting the right modem and router for your network, you can ensure a seamless and secure networking experience.

Credit: www.wired.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is Router In Networking And How It Works
How Router Works Step By Step?
A router works by connecting devices in a network and managing the flow of data between them.
What Is The Difference Between A Router And A Modem?
A modem connects your home network to your internet service provider. A router lets all your devices use the internet connection and communicate with each other.
What Is A Router In Networking For Dummies?
A router is a device that provides Wi-Fi and connects to a modem, sending internet information to personal devices like computers, phones, and tablets.
Why Do We Need a Router?
A router connects devices to the internet and allows them to communicate with each other wirelessly or through an Ethernet cable.
Conclusion
A router is a crucial component of networking that plays a vital role in the efficient transmission of data between different networks. It acts as a gateway, connecting devices within a local area network (LAN) to the internet. By forwarding data packets between networks, a router ensures that information reaches its intended destination accurately and efficiently.
Routers use routing tables and protocols to determine the best path for data transmission, optimizing speed and minimizing congestion. Additionally, routers provide security features such as firewall protection and network address translation (NAT), ensuring the safety of data being transmitted.
With the increasing demand for internet connectivity and the growth of networks, routers have become an essential tool in managing and improving network performance. By understanding how routers work and their importance in networking, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions to enhance their internet connectivity and optimize network performance.